SPOTLIGHT
Letter from Dr. Stephen I. Katz: Showcasing NIAMS Research in Action for Key Stakeholders
Dear Colleagues,
A key part of the NIAMS mission is keeping our stakeholders informed of the accomplishments made possible through the investment of the American peoples’ tax dollars in biomedical research, and how that research is improving the lives of people living with diseases and conditions of the bones, joints, muscles and skin. NIAMS interacts with multiple groups, including investigators and grantees, and professional and voluntary organizations that represent the interests of scientists, medical practitioners and patients. Another important group that we interact with frequently is Congressional staff.
Image: Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D.
NEWS
PMI Cohort Program Announces New Name: The All of Us℠ Research Program
The Precision Medicine Initiative® Cohort Program (PMI) will be the largest health and medical research program of its kind. To truly reflect the far-reaching nature of the program, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) developed a name that would convey the inclusivity and openness that are hallmarks of the PMI research program.
NIH Funds Additional Medical Centers To Expand National Precision Medicine Research Program
The NIH announced awards to add four regional medical center groups to the national network of health care provider organizations that will implement the Precision Medicine Initiative® Cohort Program, recently renamed the All of Us℠ Research Program. They are the California Precision Medicine Consortium, Geisinger Health System, New England Precision Medicine Consortium and the Trans-American Consortium for the Health Care Systems Research Network.
NIAMS’ O’Shea Honored for Outstanding Interferon and Cytokine Research
NIAMS Scientific Director John J. O’Shea, M.D., has been awarded the 2016 Seymour and Vivian Milstein Award by the International Cytokine and Interferon Society (ICIS). The award, conferred at the 2016 ICIS annual meeting on October 16, 2016, recognizes achievements by biomedical researchers "who have made outstanding contributions to cytokine and interferon research, either in a basic or applied field."
Image: John O’Shea, M.D., (l) receives his award from ICIS President Tada Taniguchi, Ph.D.
NIAMS Announces New Centers of Research Translation
The NIAMS announced four new Centers of Research Translation (CORT) awards. CORTs are team science programs designed to address translational research challenges in diseases or conditions within the mission of the NIAMS. They are:
- Alopecia Areata Center of Research Translation
- Center for Lupus Research
- Center of Research Translation in Muscular Dystrophy Therapeutic Development
- University of Michigan Fibromyalgia CORT
NIH Common Fund Announces 2016 High-Risk, High-Reward Research Awards
The High-Risk, High-Reward Research program, supported by the NIH Common Fund, awarded 88 grants to highly creative and exceptional scientists with bold approaches to major challenges in biomedical research. The awards span the broad mission of the NIH and include groundbreaking research, such as engineering immune cells producing drugs at the site of diseased tissue, developing a sensor to rapidly detect antibiotic resistance of a bacterial infection, understanding how certain parasites evade host detection by continually changing their surface proteins and developing implants that run off the electricity generated from the motion of a beating heart. The NIH Common Fund will hold the 2016 High-Risk, High-Reward Research Symposium from December 5–7 on the NIH Main Campus in Bethesda, MD.
Creative Minds: Can Diseased Cells Help To Make Their Own Drugs?
With funding from a 2015 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award, Matthew Disney, Ph.D., is applying his ingenious approach to drug delivery to treat a common form of muscular dystrophy. He also plans to test the strategy’s potential for other disorders including Huntington’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Image: Matthew Disney, Ph.D., Scripps Research Institute.
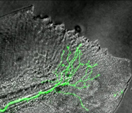
Cool Videos: Regenerating Nerve Fibers
The zebrafish is among the few vertebrates that can regrow body parts after they’ve been badly damaged or even lost. Using time-lapse photography over a period of about 12 hours, NIH grantee Sandra Rieger, Ph.D., used a fluorescent marker (green) to track a nerve fiber spreading through the skin of a zebrafish tail fin (gray). Along with other tools, Rieger is using such imaging to explore how the processes of nerve regeneration and wound healing are coordinated.
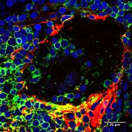
Studies Provide Evidence for Long-Suspected Role of Viral Infections in Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the glands that produce tears and saliva. The causes of Sjögren’s have been somewhat elusive, but it is thought to involve both environmental and genetic factors. Now, two new studies by researchers at the NIH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) provide insight into the roles played by two viruses.
Image: B cells (red and green) line the rim of a salivary duct in salivary gland tissue from a Sjögren’s syndrome patient. B cells are thought to contribute to the disease. Photo credit: Ilias Alevizos, D.M.D., M.M.Sc., NIDCR.
FDA Approves Amjevita, a Biosimilar to Humira
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) as a biosimilar to Humira (adalimumab) for multiple inflammatory diseases.
FDA Approves Expanded Indications for Ilaris for Three Rare Diseases
The FDA approved three new indications for Ilaris (canakinumab). The new indications are for rare and serious auto-inflammatory diseases in adult and pediatric patients:
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS)
- Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome (HIDS)/Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD)
- Familial Mediterranean Fever
All three syndromes are hereditary diseases characterized by periodic attacks of fever and inflammation, as well as severe muscle pain. There are no previously approved therapies for TRAPS or HIDS/MKD.
FDA Awards 21 Grants To Stimulate Product Development for Rare Diseases
The FDA announced that it awarded 21 new clinical trial research grants totaling more than $23 million over the next four years to boost the development of products for patients with rare diseases. Six of the 21 awards are for conditions of the bones, muscles, joints or skin.
RESOURCES
Spotlight on Scientific Imagery: Nanoparticles Reduce Joint Inflammation After Injury
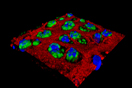
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that injecting nanoparticles into an injured mouse joint can inhibit the inflammation that damages the cartilage and leads to the development of osteoarthritis (OA). The nanoparticles carry a peptide into the cells, interfering with the process of inflammation. Shown in green is an inflammatory protein, NF-κB, in cartilage cells (blue) of an injured joint. After the nanoparticles were injected, the inflammation was greatly reduced. This study may help researchers develop treatments that reduce or prevent the development of OA in injured joints. This image is courtesy of Christine Pham, M.D., Washington University School of Medicine.
Implementing New Rigor and Transparency Policies in Review—Lessons Learned at the NIH Center for Scientific Review
Grant reviewers have completed their first round of grant reviews since NIH established new guidelines to improve rigor and transparency. Find out how they met the challenge of reviewing applications incorporating the changes to enhance research rigor and transparency.
Videocast: Opioids for Chronic Pain: Evidence, Guidelines, and Policy and Practice Implications
This presentation by Roger Chou, M.D., reviews epidemiological data on opioid prescribing; the evidence on benefits and harms of opioid therapies; and recently released guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on use of opioids for chronic pain. Dr. Chou is the lead author on a systematic review of opioids for chronic pain conducted for an NIH Pathways to Prevention workshop and an author of the CDC guidelines.
CDC: Falls and Fall Injuries Among Adults Aged ≥ 65 Years—United States, 2014
This CDC study estimates the numbers, percentages and rates of falls and fall injuries among older adults by selected characteristics and state. In 2014, 28.7 percent of older adults reported falling; the estimated 29 million falls resulted in 7 million injuries.
CDC: Prevalence of Severe Joint Pain Among Adults With Doctor-Diagnosed Arthritis—United States, 2002–2014
This CDC study found that almost 15 million U.S. adults with arthritis have severe joint pain that can limit their ability to perform basic functions and seriously compromise their quality of life. The report recommends that health care professionals begin to implement the 2016 National Pain Strategy objectives of taking steps to reduce barriers to pain care and increasing patient knowledge of treatment options and risks.
Use of Complementary Health Approaches for Musculoskeletal Pain Disorders Among Adults: United States, 2012
In 2012, more than half of adults in the U.S. had a musculoskeletal pain disorder like arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome, according to data from the CDC [PDF – 304 KB]. Nearly 42 percent of those people turned to complementary health approaches, whether for their pain disorders or for another reason.
EVENTS
NIH Common Fund High-Risk, High-Reward Research Symposium
December 5–7, 2016
Natcher Conference Center (Building 45)
NIH Campus, Bethesda, MD
Agenda
Registration is required.
The event will be videocast.
NIH Science Lectures and Events Available via Internet
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video (videocast). The NIH calendar notes these videocast events with a video icon ![]() .
.
Funding Announcements
If you would like information about funding opportunities, please view the NIH Guide for Grants and Contracts, the primary source for information about NIH funding opportunities. You can also request a weekly Table of Contents from the NIH Guide. In addition, the NIAMS website provides comprehensive information on NIAMS-related grants and processes.