SPOTLIGHT
Letter from Dr. Stephen I. Katz: NIH Tools That Ensure Transparency and Accountability
Dear Colleagues,
The NIAMS has a three-pronged mission: to support research into the causes, treatment, and prevention of arthritis, musculoskeletal and skin diseases; to train the next generations of researchers; and to disseminate information about research progress. We are held accountable for how we spend more than $500 million annually in taxpayer funds, and sharing that information is a critical component of our communications efforts. NIAMS and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have a variety of resources available to provide transparency on the projects and programs we support.
Image: Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D.
NEWS
NIH Names Nationwide Partners for Precision Medicine Initiative Cohort Program
The NIH announced awards for partnerships and infrastructure needed to launch the Cohort Program of President Obama’s Precision Medicine Initiative (PMI). The PMI Cohort Program is a research effort that aims to engage 1 million or more U.S. participants to improve our ability to prevent and treat disease based on individual differences in lifestyle, environment and genetics. Visit the NIH’s PMI Cohort Program website to learn more about the program.
NIAMS Awards Five New Supplements to Advance Research (STAR) To Support Early Stage Scientists: Program Is Part of Broader NIH Efforts To Foster the Next Generation of Biomedical Researchers
In February 2015, NIAMS launched the Supplements to Advance Research, or STAR, awards program to provide additional support for early career-stage investigators. The Institute awarded the first three STAR awards in July 2015. Recently, the NIAMS awarded STAR supplements to five more investigators.
Research Innovation for Scientific Knowledge Funding Opportunities Announced
The NIAMS Research Innovation for Scientific Knowledge (RISK) initiative focuses on innovative research within the NIAMS mission by encouraging applicants to pursue unusual observations, test imaginative hypotheses, investigate creative concepts and build ground-breaking paradigms, all of which deviate significantly from the current prevailing theories or practice. More information on the RISK Funding Opportunity Announcements are available:
- Pre-application: Research Innovation for Scientific Knowledge for Skin and Rheumatic Diseases (X02)
- Research Innovations for Scientific Knowledge for Skin and Rheumatic Diseases (R61/R33)
- Pre-application: Research Innovation for Scientific Knowledge for Musculoskeletal Diseases (X02)
- Research Innovations for Scientific Knowledge for Musculoskeletal Diseases (R61/R33)
NIAMS Director Issues Statement on FY 2017 Budget Request
NIAMS Director Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D., released a prepared statement for the record on the President’s Fiscal Year (FY) 2017 budget request for the NIAMS. The statement describes NIAMS investments in basic and clinical research, as well as its commitment to the study of biomarkers, and to fostering innovation and enhancing stewardship.
Ion Channel Found To Play Role in Itch Sensation
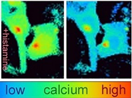
Two independent teams of investigators funded in part by the NIAMS have discovered that a molecule called TRPV4 plays a role in sensing itch. The researchers found that TRPV4 responds to certain itch-inducing substances by sending a signal to the brain, where sensations are “felt.”
Image: Skin cell of a mouse shows the flow of calcium into the cell in response to histamine (left panel). An ion channel called TRPV4 is the beginning of a chain of messages that signals “itch” to the brain. Photo credit: Yong Chen, Ph.D., and Wolfgang Liedtke, M.D., Ph.D., Duke University.
Space Experiment on Bone Health Successfully Launched Into Orbit
On July 20, the SpaceX Dragon capsule met up with the International Space Station to deliver special cargo—materials for a new study on the effects of microgravity on bone cells. Funded by the NIH’s National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), the research is part of a program of collaboration between the NIH and NASA.
Image: The International Space Station orbits Earth, where astronauts complete an array of scientific experiments. Photo credit: NASA.
Scoliosis Traced to Problems in Spinal Fluid Flow
Most cases of scoliosis in children occur for unknown reasons. A new NIH-funded study involving zebrafish offers a surprising explanation. It points to the possibility of developing precisely targeted therapeutics to reduce or even prevent scoliosis.
Stem Cell Research: New Recipes for Regenerative Medicine
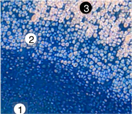
To help people suffering from a wide array of injuries and degenerative diseases, scientists and bioengineers have long dreamed of creating new joints and organs using human stem cells. Now, an NIH-funded team of researchers has reported important progress on this front.
Image: Human bone cell progenitors, derived from stem cells, were injected under the skin of mice and formed mineralized structures containing cartilage (1-2) and bone (3). Photo credit: Kyle Loh, Angela Chen, et. al., Stanford University.
Manufactured Stem Cells To Advance Clinical Research: Clinical-Grade Cell Line Will Enable Development of New Therapies and Accelerate Early-Stage Clinical Research
Supported by the NIH Common Fund’s Regenerative Medicine program, researchers have developed a clinical-grade stem cell line, which has the potential to accelerate the advance of new medical applications and cell-based therapies for people who have ailments such as muscular dystrophy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury and diabetes.
Spotlight on Psoriasis: Preventing Patches of Itchy, Sore Skin
Psoriasis is a long-term, or chronic, skin disorder that affects more than 6.7 million U.S. adults. Symptoms can vary, but it’s usually recognized by itchy or sore patches of thick, red skin with silvery scales. There’s currently no cure, but treatment often helps.
Juvenile Arthritis: Discoveries Lead to Newer Treatments
Juvenile arthritis is one of the most common chronic illnesses affecting children. Symptoms include joint pain, inflammation (swelling), tenderness and stiffness. One early sign may be limping in the morning.
FDA Approves Differin Gel 0.1% for Over-The-Counter Use To Treat Acne: First Retinoid Approved for Over-The-Counter Use
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Differin Gel 0.1% (adapalene), a once-daily topical gel for the treatment of acne. Differin Gel 0.1% is approved for use in people 12 years of age and older.
FDA Approves New Medication for Dry Eye Disease
The FDA approved Xiidra (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) for the treatment of signs and symptoms of dry eye disease. Xiidra is the first medication in a new class of drugs, called lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 agonists, approved by the FDA for dry eye disease.
FDA Approves an Increase to the Amount of Vitamin D for Milk and Milk Alternatives
The FDA approved an increase to the amount of vitamin D that may be added as an optional ingredient to milk, and approved the addition of vitamin D to beverages made from edible plants intended as milk alternatives, such as beverages made from soy, almond and coconut, and edible plant-based yogurt alternatives.
2018 Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Announced
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Service’s Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion announced the members of the 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee. During their two-year term, the Advisory Committee members will collaborate on the development of the second edition of the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
RESOURCES
Spotlight on Scientific Imagery: Cultured Muscle Microtubules
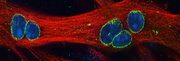
Cultured muscle cells form myotubes, which are long cells with multiple nuclei. The formation of myotubes mimics the differentiation of muscle in animals, except that cultured myotubes never develop much further than this point. Muscle cultures are helpful in understanding the role and organization of cellular structures which are affected in muscle diseases. This image shows microtubules (in red), which are long protein filaments that have been implicated in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Microtubules grow from protein complexes that contain the protein pericentrin (green). Microtubules and pericentrin are completely reorganized during muscle differentiation. This image is courtesy of Evelyn Ralston, Ph.D., of the NIAMS Light Imaging Section, and is in the public domain.
Watch NIAMS Patient Experiences: Lupus Patient Video
(Spanish Captions Available)

Nicole, who is living with lupus, shares her experience as a patient enrolled in a NIAMS clinical study at the NIH Clinical Center.
Watch NIAMS Patient Experiences: Giant Cell Arteritis Patient Video
(Spanish Captions Available)

LaZann, who is living with giant cell arteritis—a type of vasculitis—shares her experience as a patient enrolled in a NIAMS clinical study at the NIH Clinical Center.
Study Results From the Bone Quality Project Now Available
The Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) Biomarkers Consortium recently released the first study results from the Bone Quality Project, which analyzed bone mineral density as a biological marker (biomarker) for predicting hip fractures. Dennis Black, Ph.D., Principal Investigator of the FNIH Biomarkers Consortium’s Bone Quality Project, discusses study findings in this Q&A.
EVENTS
September NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting
The NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting will be held September 13, 2016, in Building 31, 6th Floor, C Wing, Conference Room 6, NIH Campus, Bethesda, MD. A meeting agenda is available. This Council meeting will be available for live viewing via the NIH videocasting service as well.

NIH Science Lectures and Events Available via Internet
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video (videocast). The NIH calendar notes these videocast events with a video icon ![]() .
.
Funding Announcements
If you would like information about funding opportunities, please view the NIH Guide to Grants and Contracts, the primary source for information about NIH funding opportunities. You can also request a weekly Table of Contents from the NIH Guide. In addition, the NIAMS website provides comprehensive information on NIAMS-related grants and processes.