Spotlight
Letter from Dr. Stephen I. Katz: New NIAMS Initiative Facilitates Transition From Projects to Programs
Although we are living in a time of unprecedented scientific opportunities, the funding climate has become increasingly challenging for researchers. In light of this issue, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and its individual Institutes have begun considering a range of options to enhance research funding stability and flexibility. The proposals on the table are diverse. Institutes are considering using different funding mechanisms that target investigators at specific career stages. For example, some Institutes are designing programs for early-career stage investigators, while others are focusing their efforts on more senior scientists.
Image: Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D.
News
 Halting Inflammation After Joint Injury May Reduce Risk of Osteoarthritis Later
Halting Inflammation After Joint Injury May Reduce Risk of Osteoarthritis Later
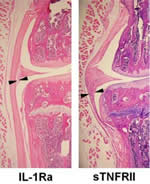
Injecting an inflammation-blocking medication into a joint area immediately following an injury prevents the onset of post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA) in mice and may lead to new treatments for patients, according to a study funded in part by the NIAMS. The study was published in the journal, Arthritis Research & Therapy. It is common for people to experience joint deterioration after a bone fracture or from a ligament or meniscal tear. Some go on to develop PTOA, but the progression over time is not well understood.
Image: IL-1-treated cartilage vs. TNF-treated cartilage. Photo credit: Farshid Guilak, Ph.D., Duke University.
Serotonin Drives Vicious Cycle of Itching and Scratching
Scratching an itch brings short-lived relief but often makes the itching worse in the long term. Now, a team of investigators led by Zhou-Feng Chen, Ph.D., director of the Center for the Study of Itch at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, and supported in part by the NIAMS, has uncovered an explanation.
Chronic Low-Back Pain Research Standards Announced by NIH Task Force
Recommended standards for clinical low-back pain research hold promise for more consistently designed research and, in the long term, better treatment solutions to support those living with chronic low-back pain. The recommendations from the NIH Task Force on Research Standards for Chronic Low-Back Pain, which were supported in part by the NIAMS, were published in several leading back pain journals.
New Study Published on Marfan Syndrome
Between 70 and 80 percent of patients with the connective tissue condition Marfan syndrome have aortic-root dilation, which happens when the aorta, the main blood vessel between the heart and body, becomes too large and tears. This condition can result in serious illness and sometimes death. A study funded by the NIH comparing treatment with widely used blood pressure medications atenolol or losartan in patients with Marfan syndrome who had an enlarged aortic root found no significant difference in the rate of aortic-root dilation between the two treatment groups over three years.
The Skin Microbiome: More Than Skin Deep
The billions of microbes that reside on human skin—probably more than 10 billion microbial cells on each of us—may be fellow travelers, but they aren’t free riders. Instead, the skin microbiota plays an intricate role in the human immune system, actually directing many immune functions and helping to defend its host against invading bacterial pathogens. In a review article in the Nov. 21, 2014, issue of Science, NIH scientists sum up what researchers have learned so far about the advantages, and some of the downsides, of this intimate partnership.
New Comprehensive View of the Mouse Genome Finds Many Similarities and Striking Differences With Human Genome
Looking across evolutionary time and the genomic landscapes of humans and mice, an international group of researchers has found powerful clues to why certain processes and systems in the mouse—such as the immune system, metabolism and stress response—are so different from those in people. Building on years of mouse and gene regulation studies, they have developed a resource that can help scientists better understand how similarities and differences between mice and humans are written in their genomes.
NIH Research Featured In National Geographic Channel Documentary on Sleep
The NIH, in partnership with the National Geographic Channel and The Public Good Projects, will draw the nation’s attention to the health consequences of sleep deprivation and what keeps Americans up at night. The documentary, “Sleepless in America,” premiered on the National Geographic Channel on November 30. For more information about “Sleepless in America” showtimes and online availability, visit this NIH webpage. The NIAMS has also invested in sleep research. In 2013, the NIAMS reported on a study about pain processing and sleep disturbance. Also in 2013, the NIAMS sponsored a retreat to explore the importance of circadian regulation in NIAMS’ mission areas.
NIH Takes Step To Speed the Initiation of Clinical Research by Ensuring Use of Single IRB
The NIH issued a draft policy to promote the use of single institutional review boards, or IRBs, in multisite clinical research studies. IRBs play a critical role in assuring the ethical conduct of clinical research, and studies must be reviewed and approved by an IRB before they can begin. When the regulations for protection of human subjects were first published, most clinical research was conducted at a single institution. Since then, the research landscape has evolved, and many studies are carried out at multiple sites and within large networks. Studies that go beyond a single site are often able to recruit more individuals from diverse populations. These studies can often generate important results in less time. However, working through an IRB review at each site can add delay without increasing the protections for the research participants in the study.
Proposed Principles and Guidelines for Reporting Preclinical Research
Earlier this year, the NIH held a joint workshop with the Nature Publishing Group and Science on the issue of reproducibility and rigor of research findings, with journal editors representing over 30 basic/preclinical science journals in which NIH-funded investigators have most often published. Science, Nature and many other journals have agreed to the Proposed Principles and Guidelines for Reporting Preclinical Research, which includes the importance of reporting the sex of animals involved in research.
A Proposed Regulation and Policy To Further the Impact of Clinical Trials Research
Clinical trials play a vital role in transforming scientific research into medical interventions to improve human health. Transparency about the clinical trials underway and their subsequent results ensure potential participants can make informed decisions about enrolling in clinical trials and know how their participation may have helped others.
NIH Director’s Blog
Genome Sequencing: Exploring the Diagnostic Promise
When a draft of the 3 billion letters of the human genome was completed about a decade ago, it would have cost about $100 million to sequence a second human genome. Today, thanks to advances in DNA sequencing technology, it will soon be possible to sequence a person’s genome for $1,000 or less. All of this progress has made genome sequencing a far more realistic clinical option to consider for people, especially children, who suffer from baffling disorders that can’t be precisely diagnosed by other medical tests. This work was supported in part by the NIAMS.
 Honoring Our Promise: Clinical Trial Data Sharing
Honoring Our Promise: Clinical Trial Data Sharing
When people e nroll in clinical trials to test new drugs, devices or other interventions, they’re often informed that such research may not benefit them directly. But they’re also told what’s learned in those clinical trials may help others, both now and in the future. To honor these participants’ selfless commitment to advancing biomedical science, researchers have an ethical obligation to share the results of clinical trials in a swift and transparent manner.
Other Federal News
 Quick Health Data Online From the HHS Office on Women’s Health
Quick Health Data Online From the HHS Office on Women’s Health
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office on Women’s Health has developed Quick Health Data Online, an online database that offers extensive information on a variety of health and health-related topics. The system provides state- and county-level data for all 50 states, the District of Columbia and U.S. territories and possessions. Data are available by gender, race and ethnicity and come from a variety of national and state sources. The website explains the data sources and data analysis methods. The system documentation and Frequently Asked Questions provide additional details on calculation of various indicators, frequency of system updates and more.
Gather and Share Your Family Health History
If you are concerned about a disease running in your family, collect your family health history and talk to your doctor at your next visit. A doctor can evaluate all of the factors, including family health history, which may affect your risk of diseases, and can recommend ways to reduce that risk. Other HHS family health history resources include: the Surgeon General’s Family Health History Initiative, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Office of Public Health Genomics and the National Human Genome Research Institute’s Family History webpage.
CDC—Antibiotics Aren’t Always the Answer
Antibiotics do not fight infections caused by viruses like colds, flu, most sore throats, bronchitis, and many sinus and ear infections. Instead, symptom relief might be the best treatment option for viral infections. Get smart about when antibiotics are needed—to fight bacterial infections. When you use antibiotics appropriately, you do the best for your health, your family’s health and the health of those around you.
FDA Approves Extended-Release, Single-Entity Hydrocodone Product With Abuse-Deterrent Properties
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) today approved Hysingla ER (hydrocodone bitartrate), an extended-release (ER) opioid analgesic to treat pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. Hysingla ER has approved labeling describing the product’s abuse-deterrent properties consistent with the FDA’s 2013 draft guidance for industry, Abuse-Deterrent Opioids—Evaluation and Labeling [PDF - 462 KB].
NEW PUBLICATIONS AND PRODUCTS
Order Your 2015 A Year of Health Planners Today!
We are excited to announce that as part of the National Multicultural Outreach Initiative (NMOI), the NIAMS has created free multicultural health planners for 2015! For the third consecutive year, these planners continue to provide research-based health tips and information about staying healthy and managing conditions of the bones, joints, muscles and skin.
They also include space to write down notes and stickers to track medications, health appointments and other important dates. With a new year quickly approaching, we invite you to prepare yourself, your family and your community for another year of health in 2015. Planners have arrived and will not last long, so order yours today!
Organizations can order up to 200 free A Year of Health planners. For more information or to place your order, visit the NIAMS NMOI website.
Three NIAMS Studies Currently Recruiting at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland
Studies of the Natural History, Pathogenesis and Outcome of Idiopathic Systemic Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of diseases that inflame and damage blood vessels and tissue. Few tests can diagnose the disease, and none can reliably predict a relapse. Researchers want to study people’s genes and follow people over time to see how the disease affects them. In addition, researchers want to learn what causes vasculitis, learn what markers in blood might help doctors treat vasculitis, and use imaging scans to view blood vessels affected by vasculitis.
Safety and Tolerability of Omalizumab in Patients With Lupus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE or lupus) is an autoimmune disease that can affect almost any organ. Its symptoms can range in severity from mild to life-threatening and can vary from person to person. Current treatments for lupus are not effective for some people. Omalizumab, a drug that reduces IgE antibodies in the blood, has been used to treat severe asthma. IgE antibodies are also present in some people with lupus, and researchers want to see if omalizumab is a safe and effective treatment for people with lupus.
Study of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
This protocol will evaluate patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and their relatives to learn more about how the disease develops and changes over time. It will also study genetic factors that make a person susceptible to SLE. Patients 10 years of age and older with known or suspected SLE and their relatives may be eligible for this study.
NLM’s Circulating Now
Want a glimpse into the National Library of Medicine’s (NLM’s) massive history of medicine collections that encompass millions of items spanning 10 centuries? Sure, you could visit the NLM in person, but there’s another way to explore some of its vast holdings that are in every form you can imagine—books, journals, photographs, lantern slides, motion picture films, audio and video recordings, ephemera, portraits, lithographs, digital materials and more—from the comfort of your home or office. Check out NLM’s Circulating Now blog.
NIH Research Matters
NIH Research Matters is a review of NIH research from the Office of Communications and Public Liaison, Office of the Director, NIH.
NIH News in Health
Read practical health information in NIH News in Health, which is reviewed by the NIH’s medical experts and is based on research conducted either by the NIH’s own scientists or by its grantees at universities and medical schools around the country.
When Your Back Hurts
Is your back hurting? You’re in good company. In any 3-month period, about 1 in 4 adults in the U.S. has at least 1 day of back pain, mostly in the lower back.
MEETINGS
February NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting
The NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting will be held February 4, 2015, in Building 31, 6th Floor, C Wing, Conference Room 6, NIH Campus. A meeting agenda will be posted as soon as it is available.

Rare Disease Day at NIH
Friday, February 27, 2015
8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.
Masur Auditorium (Building 10)
Cost: free
A meeting agenda will be posted as soon as it is available.
Available by videocast.
NIH Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series
The NIH’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series offers weekly lectures every Wednesday at 3 p.m. in Masur Auditorium, Building 10, NIH Campus. Renowned scientists from around the globe present research on a variety of topics. The lectures are Continuing Medical Education-certified, open to the public and available live via webcast.
Upcoming Lecture:
January 28, 2015
Arturo Casadevall, Albert Einstein College of Medicine
“Insights Into Microbial Pathogenesis and Immunology From Cryptococcus Neoformans”
NIH Science Lectures and Events Available via Internet
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video. You can watch an event at your convenience as an on-demand video or a downloadable podcast. Most events are available to all; a few are broadcast for the NIH or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and are marked as such. See additional details on events.
FUNDING ANNOUNCEMENTS
NIH Funding Opportunities Now Available in RSS (Really Simple News Syndication) Format
You can now get the very latest funding opportunities published in the “NIH Guide for Grants and Contracts” in RSS format. Point your news aggregator to https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/newsfeed/fundingopps.xml and you will find the very latest Request for Applications, Program Announcements and Notices to be published each week. This list is “up to the minute”, so you know you will always be up to date. This RSS feed contains the same information found at https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/WeeklyIndex.cfm.
NIAMS Announcements
Administrative Supplements for Research on Sex/Gender Differences (Admin Supp)
(PA-15-034)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Date: January 12, 2015
NIH Common Fund Initiative Announcement
Collaborative Activities To Promote Metabolomics Research (Admin Supp)
(PA-15-030)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Date: February 13, 2015
Request for Information (RFI): Input on Direction of the Second Phase of the “Illuminating the Druggable Genome” Program
(NOT-RM-14-018)
Notice of Intent To Publish a Funding Opportunity Announcement for NIH Science of Behavior Change Resource and Coordinating Center (U01)
(NOT-RM-15-006)
Request for Information (RFI): Challenges and Opportunities for Exploring and Understanding the Epitranscriptome
(NOT-RM-15-007)
Other Funding Announcements
NIH Implementation of the U.S. Government Policy on Institutional Oversight of Life Sciences Dual Use Research of Concern
(NOT-OD-15-017)
Publication of Notice of Proposed Rulemaking for Clinical Trials Registration and Results Submission Under FDAAA
(NOT-OD-15-018)
NIH Request for Public Comments on the Draft NIH Policy on Dissemination of NIH-Funded Clinical Trial Information
(NOT-OD-15-019)
Request for Information (RFI): Inviting Comments and Suggestions on the Reagent-Related Barriers to Reproducible Research
(NOT-OD-15-020)
Note: Comments must be submitted electronically on the submission website.
Reminder: Annual Reports to the Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare due January 31, 2015
(NOT-OD-15-025)
Request for Comments on the Draft NIH Policy on the Use of a Single Institutional Review Board for Multisite Research
(NOT-OD-15-026)